| Problem 1 |
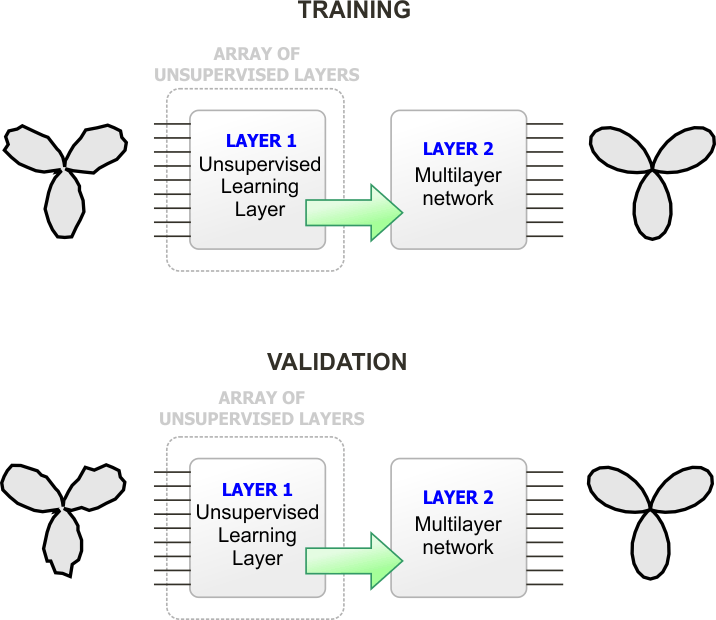
Repeat the problem in Deep Learning > Autoassociation to remove the noise from a shape using a deep learning network with supervised and unsupervised layers. Create a new project, select Deep Learning Network, General Purpose and Simulated Annealing in the new project dialog. The project name must be DeepRoseX. After creating the project, copy the following files from the DeepRose folder to the DeepRoseX folder.
Repita el problema en Deep Learning > Autoassociation para remover el ruido de una silueta una red de aprendizaje profundo con capas con y sin supervisión. Cree un nuevo proyecto, seleccione Deep Learning Network, General Purpose y Simulated Annealing en el diálogo de nuevo proyecto. El nombre del proyecto debe ser DeepRoseX. Después de crear el proyecto, copie los siguientes archivos desde la carpeta DeepRose a la carpeta DeepRoseX.
|
| Problem 2 |
| Edit the Unsuperv.lab file, then execute the code to train the RBM array using unsupervised learning. Edite el archivo Unsuperv.lab, entonces ejecute el código para entrena el arreglo de RBM usando aprendizaje sin supervisión. |
| DeepRoseX\Unsuperv.lab |
| //_______________________________________ 1. RBM Array RbmArray rbm; rbm.Create(64, 1); rbm.SetLayer(0, 1, 8); // logsig=1 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 64; i++) { rbm.SetInScaler(i, -1.0, 1.0); } //_______________________________________ 2. Load trainSetInput Matrix trainSetInput; trainSetInput.Load(); //_______________________________________ 3. Unsupervised Learning rbm.Train(trainSetInput, 1000, true); rbm.Save(); |
| Problem 3 |
| Edit the Train.lab file, then execute the code to train the layer of the network using supervised learning. Edite el archivo Train.lab, entonces ejecute el código para entrenar la capa de la red usando aprendizaje con supervisión. |
| DeepRoseX\Train.lab |
| //_______________________________________ 1. Load RBM array RbmArray rbm; rbm.Load(); //_______________________________________ 2. Compute interior input Matrix trainSetInput; trainSetInput.Load(); rbm.Train(trainSetInput, 1000, true); Matrix interior; rbm.Run(trainSetInput, interior); //_______________________________________ 3. Supervised Learning int numNeurons = rbm.GetNumOutputs(); DeepNet net; net.Create(numNeurons, 1); net.SetLayer(0, 1, 64); // logsig=1 int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 64; i++) { net.SetOutScaler(i, -1.0, 1.0); } Matrix trainSetTarget; trainSetTarget.Load(); net.SetTrainSet(interior, trainSetTarget, false); net.TrainSimAnneal( 10, //Number of Temperatures 10, //Number Iterations 15, //Initial Temperature 0.001, //Final Temperature true, //Is Cooling Schedule Linear? 1, //Number of Cycles 1.0e-5, //Goal (desired mse) true //Use Singular Value Decomposition ); net.TrainConjGrad(400,1.0e-10); //_______________________________________ 4. Save the trained network net.Save(); |
| Problem 4 |
| Edit the Refine.lab file, then execute the code to incorporate the RBM array into the deep learning network and fine tune the training. Edite el archivo Refine.lab, entonces ejecute el código para incorporar el arreglo RBM en la red de aprendizaje profundo y ajustar en forma fina el entranamiento. |
| DeepRoseX\Refine.lab |
| //_______________________________________ 1. Load RBM array RbmArray rbm; rbm.Load(); //_______________________________________ 2. Load Supervised Layers DeepNet net; net.Load(); //_______________________________________ 3. Incorporate RBM array net.AddRbmArray(rbm); //_______________________________________ 4. Load training sets Matrix trainSetInput; trainSetInput.Load(); Matrix trainSetTarget; trainSetTarget.Load(); //_______________________________________ 5. Fine tunning net.SetTrainSet(trainSetInput, trainSetTarget, false); net.TrainConjGrad(400,1.0e-10); //_______________________________________ 6. Save the trained network net.Save(); |
| Problem 5 |
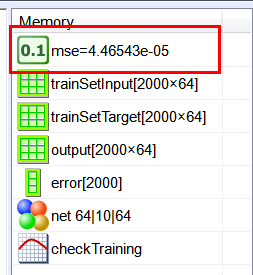
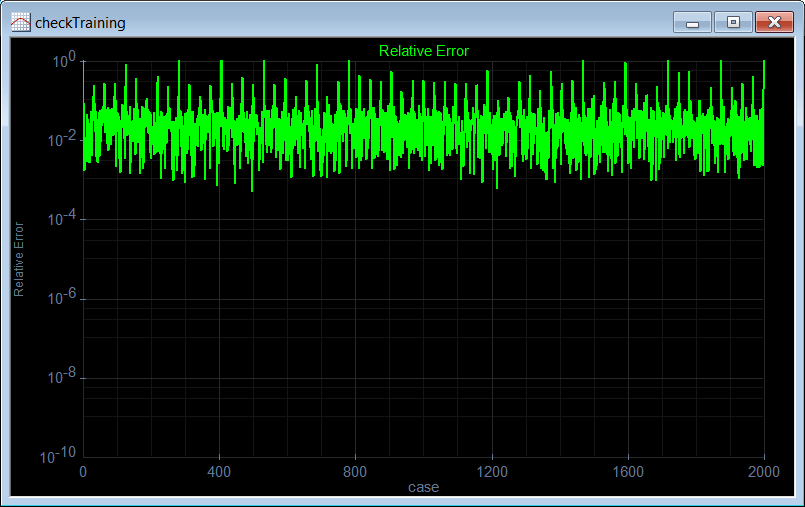
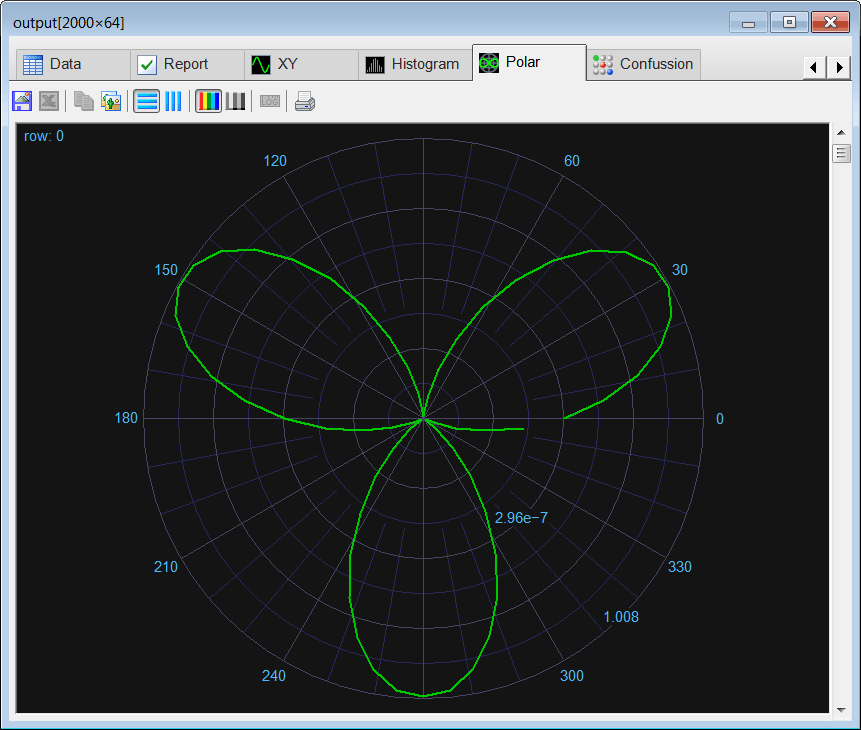
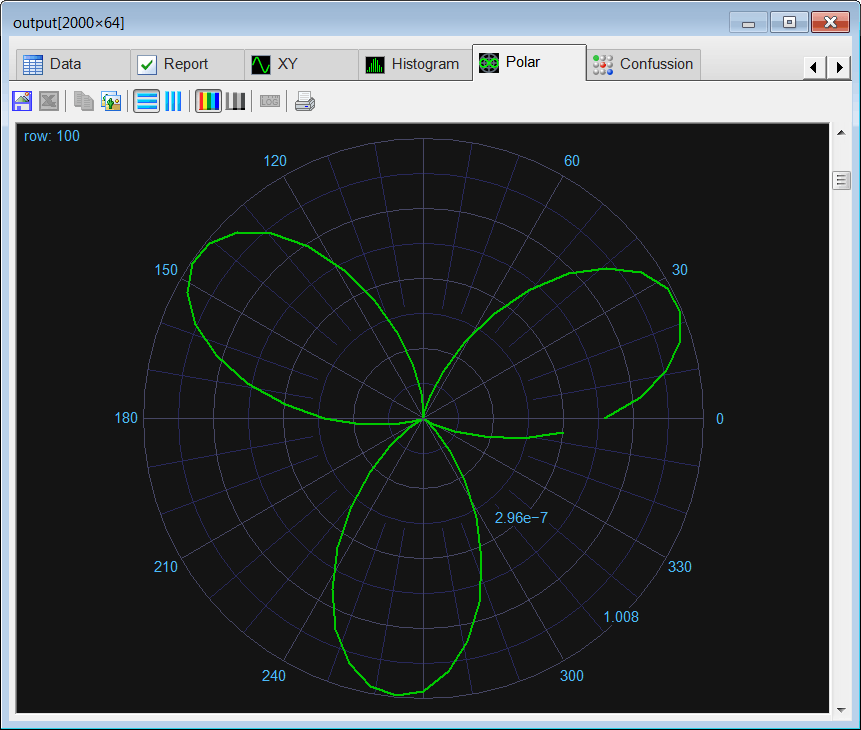
| Edit the CheckTrain.lab file, then execute the code to check the training. (a) Compute the mean squared error for the network using the training set. (b) Plot the error for each training case. (c) Save the plot as a vector image (checkTraining.pdf and checkTraining.emf) (d) Show a polar graph of the output to verify that the network has reduced the noise. Edite el archivo CheckTrain.lab, entonces ejecute el código para verificar el entrenamiento. (a) Calcule el error medio cuadrático para la red neuronal usando el conjunto de datos de entrenamiento. (b) Cree una gráfica del error para cada caso de entrenamiento. (c) Guarde la gráfica como una imagen vectorial (checkTraining.pdf y checkTraining.emf) (d) Muestre una gráfica polar de la salida para verificar que la red ha reducido el ruido. |
| DeepRoseX\CheckTrain.lab |
| //_______________________________________ 1. Load the training set Matrix trainSetInput; trainSetInput.Load(); Matrix trainSetTarget; trainSetTarget.Load(); //_______________________________________ 2. Load the network DeepNet net; net.Load(); //_______________________________________ 3. Run Matrix output; net.Run(trainSetInput, output); double mse = ComputeMse(output, trainSetTarget); //_______________________________________ 4. Relative error Vector error = ComputeRelError(output, trainSetTarget); XyChart checkTraining; checkTraining.SetCaption("case", false, "Relative Error", false); checkTraining.AddGraphY(error, "Relative Error", 2, 1, 0, 255, 0); checkTraining.SetLogScale(false, true); checkTraining.SetLimits(0, trainSetTarget.GetRowCount(), 1.0e-10, 1.0); checkTraining.SetColorMode(2); checkTraining.SaveAndShow(); checkTraining.SavePDF(0.0); checkTraining.SaveEMF(); |
| Problem 6 |
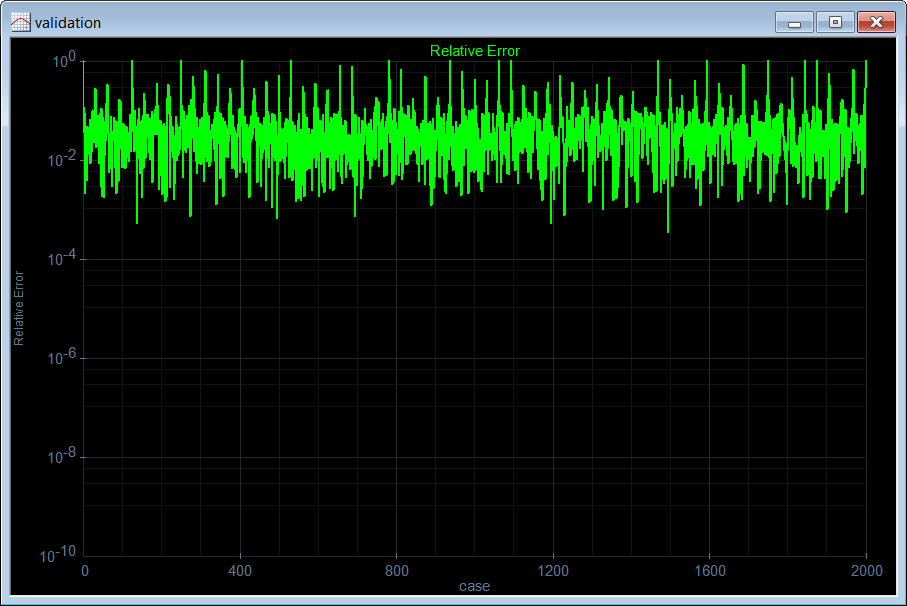
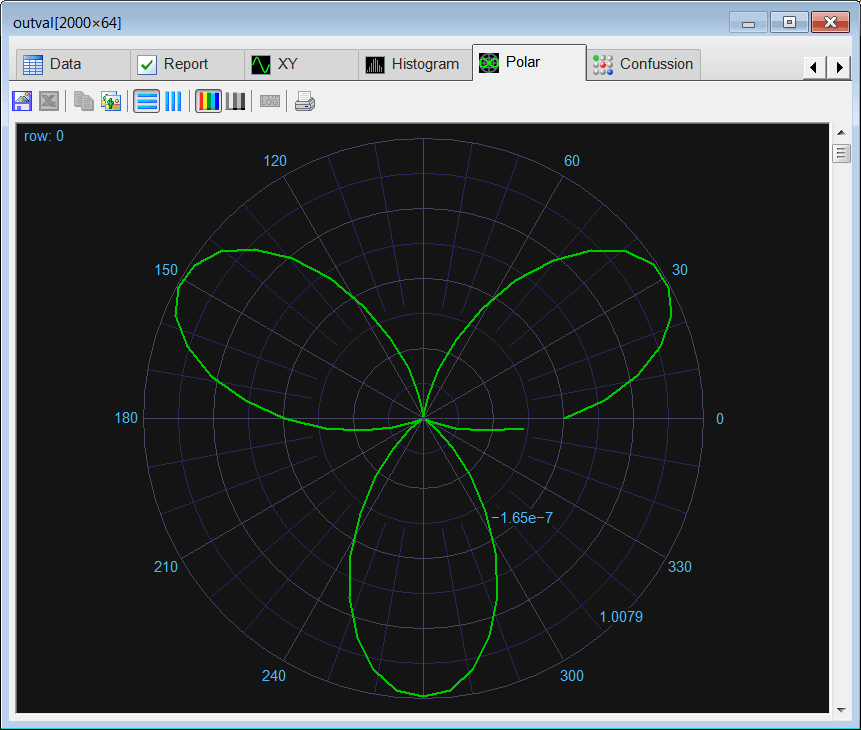
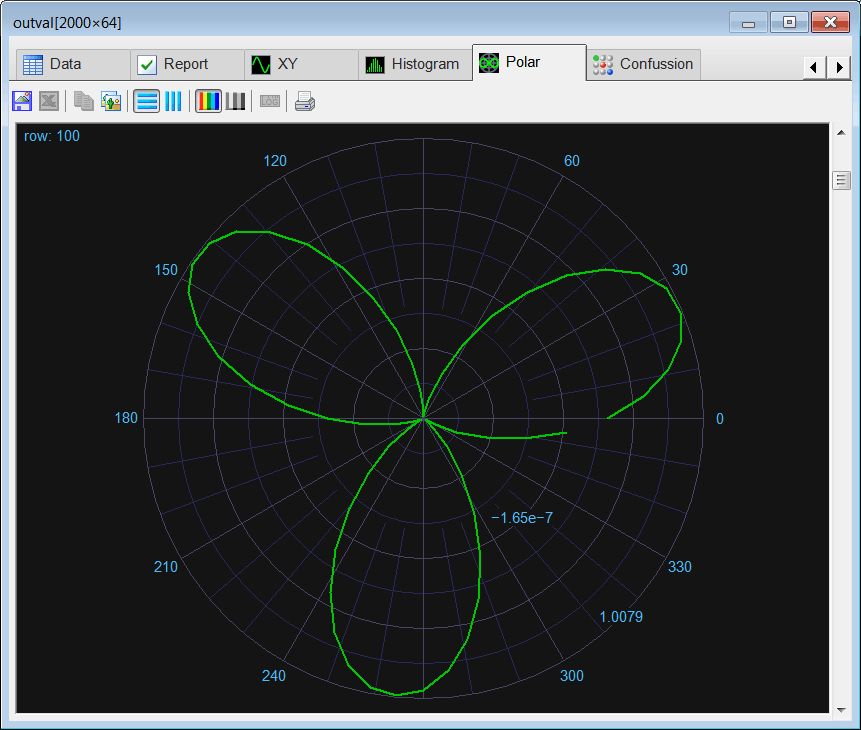
| Edit the Validation.lab file, then execute the code to validate the performance of the network. (a) Compute the mean squared error for the neural network using the validation set. (b) Plot the error for each validation case. (c) Save the plot as a vector image (validation.pdf and validation.emf) (d) Show a polar graph of the output to verify that the network has reduced the noise from the shape. Edite el archivo CheckTrain.lab, entonces ejecute el código para validar el desempeño de la red neuronal. (a) Calcule el error medio cuadrático para la red neuronal usando el conjunto de datos de validación. (b) Cree una gráfica del error para cada caso de validación. (c) Guarde la gráfica como una imagen vectorial (validation.pdf y validation.emf) (d) Muestre una gráfica polar de la salida para verificar que la red ha reducido el ruido de la silueta. |
| DeepRoseX\Validation.lab |
| //_______________________________________ 1. Load the validation set Matrix validSetInput; validSetInput.Load(); Matrix trainSetTarget; trainSetTarget.Load(); //_______________________________________ 2. Load the network DeepNet net; net.Load(); //_______________________________________ 3. Run Matrix outval; net.Run(validSetInput, outval); double mse = ComputeMse(outval, trainSetTarget); //_______________________________________ 4. Relative error Vector error = ComputeRelError(outval, trainSetTarget); XyChart validation; validation.SetCaption("case", false, "Relative Error", false); validation.AddGraphY(error, "Relative Error", 2, 1, 0, 255, 0); validation.SetLogScale(false, true); validation.SetLimits(0, trainSetTarget.GetRowCount(), 1.0e-10, 1.0); validation.SetColorMode(2); validation.SaveAndShow(); validation.SavePDF(0.0); validation.SaveEMF(); |